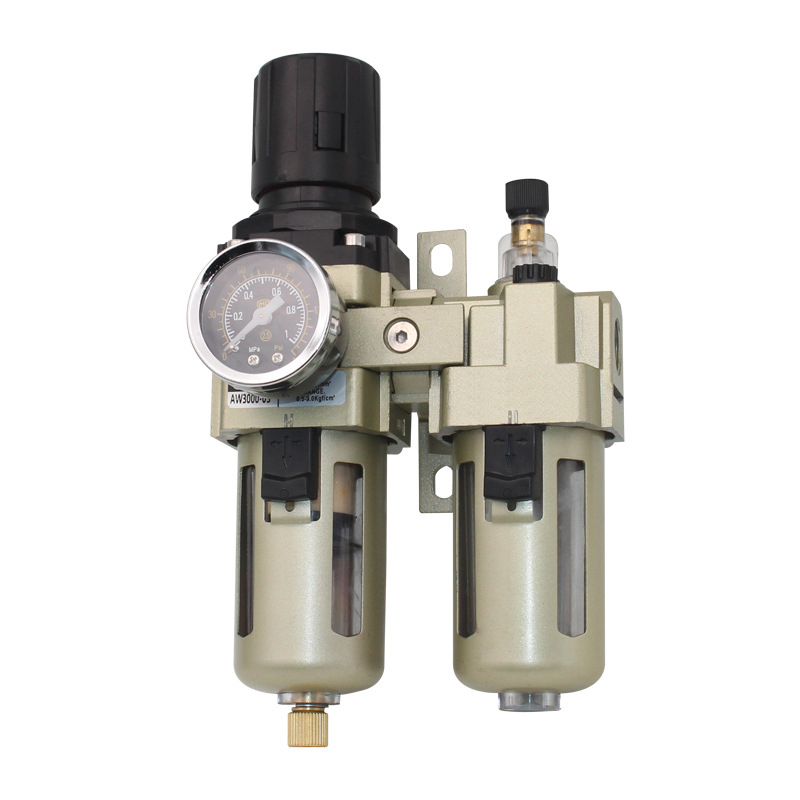
AC3010 Smc Type Pneumatic Air Source Treatment Oil Lubricator And Pressure Gauge
Selection Attention
1. How to choose the filter according to the amount of flow?
Select the appropriate flow rate according to the air consumption of the downstream equipment. Generally, we choose a filter that is slightly larger than the actual air consumption to avoid insufficient air volume and affect the operation of the equipment.There is no need to select a filter with an excessive flow rate, which will cause waste. (Refer to the flow table below for the specific flow of the product)
| Air source processor model | Interface thread | Flow |
| AC2000/AFC2000 | 1/4 =2″ | 500L/min |
| AR/AFR/AF/AL2000 | 1/4 =2″ | 500L/min |
| BC/BFC/BF/BR/BFR/BL2000 | 1/4 =2″ | 2000L/min |
| BC/BFC/BF/BR/BFR/BL3000 | 3/8=3″ | 3000L/min |
| BC/BFC/BF/BR/BFR/BL4000 | 1/2=4″ | 4000L/min |
2. How to choose the filter accuracy of the filter element?
The pore diameter of the filter element of the filter determines the filtration accuracy of the filter. Because the downstream equipment has different requirements for the quality of the gas source. For example, metallurgy, steel and other industries do not have high requirements for gas quality, so you can choose a filter with a larger filter pore size. However, industries such as medicine and electronics have high requirements for gas quality. We can choose precision filters with very small filter pores.
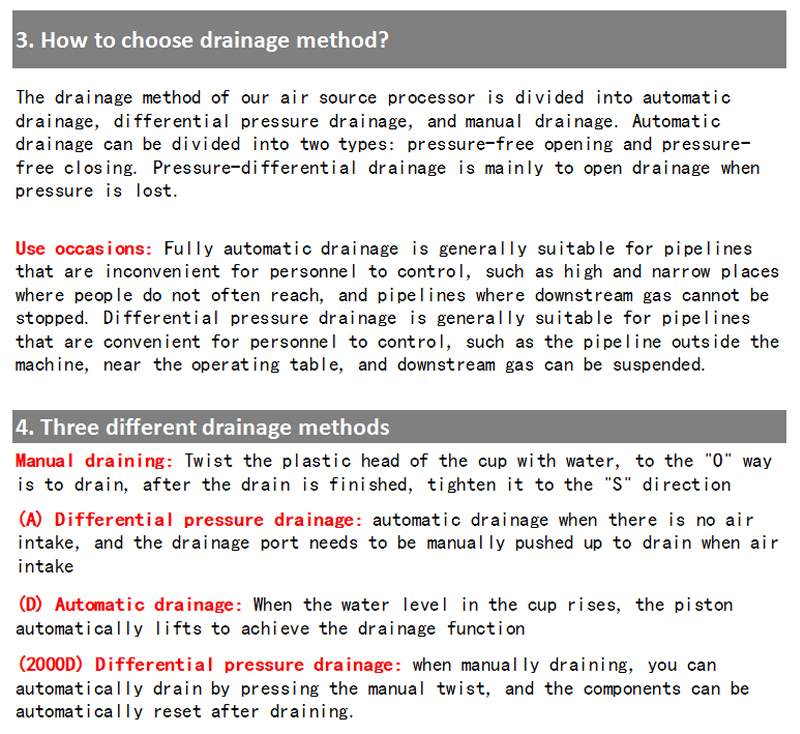
3. How to choose drainage method?
The drainage method of our air source processor is divided into automatic drainage, differential pressure drainage, and manual drainage. Automatic drainage can be divided into two types: pressure-free opening and pressure- free closing. Pressure-differential drainage is mainly to open drainage when pressure is lost.
Use occasions: Fully automatic drainage is generally suitable for pipelines that are inconvenient for personnel to control, such as high and narrow places where people do not often reach, and pipelines where downstream gas cannot be stopped. Differential pressure drainage is generally suitable for pipelines that are convenient for personnel to control, such as the pipeline outside the machine, near the operating table, and downstream gas can be suspended.
4. Three different drainage methods
Manual draining: Twist the plastic head of the cup with water, to the “0″, way is to drain, after the drain is finished, tighten it to the “S” direction
(A) Differential pressure drainage: automatic drainage when there is no air intake, and the drainage port needs to be manually pushed up to drain when air intake
(D) Automatic drainage: When the water level in the cup rises, the piston automatically lifts to achieve the drainage function
(2000D) Differential pressure drainage: when manually draining, you can automatically drain by pressing the manual twist, and the components can be automatically reset after draining.
Specification
| Proof pressure | 1.5Mpa{15.3kgf/cm²} |
| Max. working pressure | 1.0Mpa(10.2kgf/cm²} |
| Environment and fluid temperature | 5~60℃ |
| Filter aperture | 5μm |
| Suggest oil | SOVG32 Turbine 1 oil |
| Cup material | Polycarbonate |
| Cup hood | AC1000~2000 withoutAC3000~5000 with(lron) |
| Pressure regulating range | AC1000:0.05-0.7Mpa(0.51-7.1kgf/cm²)AC2000~5000:0.05~0.85Mpa(0.51~8.7kgf/cm²) |
Note:there are 2,10,20,40,70.100μmfor choose
| Model | Specification | ||||
| Minimum operating flow | The rated flow(L/min) | Port size | Cup capacity | Weight | |
| AC1000-M5 |
4 |
95 |
M5x0.8 |
7 |
0.07 |
| AC2000-02 |
15 |
800 |
1/4 |
25 |
0.22 |
| AC3000-02 |
30 |
1700 |
1/4 |
50 |
0.30 |
| AC3000-03 |
40 |
5000 |
3/8 |
50 |
0.30 |
| AC4000-03 |
40 |
5000 |
3/8 |
130 |
0.56 |
| AC4000-04 |
50 |
5000 |
1/2 |
130 |
0.56 |
| AC4000-06 |
50 |
6300 |
3/4 |
130 |
0.58 |
| AC5000-06 |
190 |
7000 |
3/4 |
130 |
1.08 |
| AC5000-10 |
190 |
7000 |
1 |
130 |
1.08 |
Air Source Treatment is a vital component of any industrial air system. It is the process of removing impurities, moisture, and other contaminants from the compressed air to ensure that it is of high quality for its intended purpose. The air we breathe is not necessarily pure, and when it is compressed for use, it is even more prone to impurities.
Air Source Treatment involves a series of operations that help to produce compressed air that is clean, dry and free of contaminants. Typically, the system comprises of filters, dryers, separators, and other essential components that work together to eliminate any harmful elements in the compressed air. Another important aspect of the treatment is the removal of excess moisture, which can cause corrosion on the air system.
The first step in air source treatment is filtration. Air filters are used to remove particulate matter such as dust, dirt and other debris. The filters trap the contaminants and prevent them from passing through to the other components of the air system. This helps to prevent premature failure of the air system and also ensures the longevity of the air compressor.
The second step is moisture removal. Moisture is one of the most common contaminants in compressed air. It can cause corrosion, and also hinder the performance of pneumatic tools and machinery. To remove moisture from the compressed air, the system uses air dryers, which work by cooling the compressed air, condensing the moisture, and draining it off.
The final step in air source treatment is oil removal. Oil can cause significant damage to the air system, and it can also contaminate the products that the compressed air is used to manufacture. To prevent this, air systems use oil separators, which filter out oils and other lubricants from the compressed air.
In conclusion, Air Source Treatment is essential for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of industrial air systems. It helps to remove impurities, excess moisture, and other contaminants from compressed air. By using filters, dryers and separators, air source treatment ensures that the compressed air is of high quality, which is essential for many industrial applications.